In an era where automotive cybersecurity has become as crucial as the vehicles’ physical mechanics, mastering the art of risk assessment and mitigation is no longer optional—it’s imperative. Enter TARA (Threat and Risk Assessment), the cornerstone of ISO 21434, a standard that revolutionizes how the automotive industry approaches cybersecurity.
The intricacies of TARA offer a comprehensive guide to navigating the challenges and best practices of ISO 21434 compliance. With Cybellum’s insights and solutions, we will explore how to adeptly maneuver through this critical landscape.
Understanding ISO 21434 Compliance
ISO 21434 is more than a guideline; it’s a comprehensive framework ensuring automotive cybersecurity from design to decommission. This standard recognizes the critical nature of cybersecurity in an age where vehicles are becoming increasingly connected and autonomous. It mandates an ongoing process of risk assessment, mitigation, and management throughout the automotive product lifecycle, ensuring that vehicles are not just safe, but also secure from cyber threats.
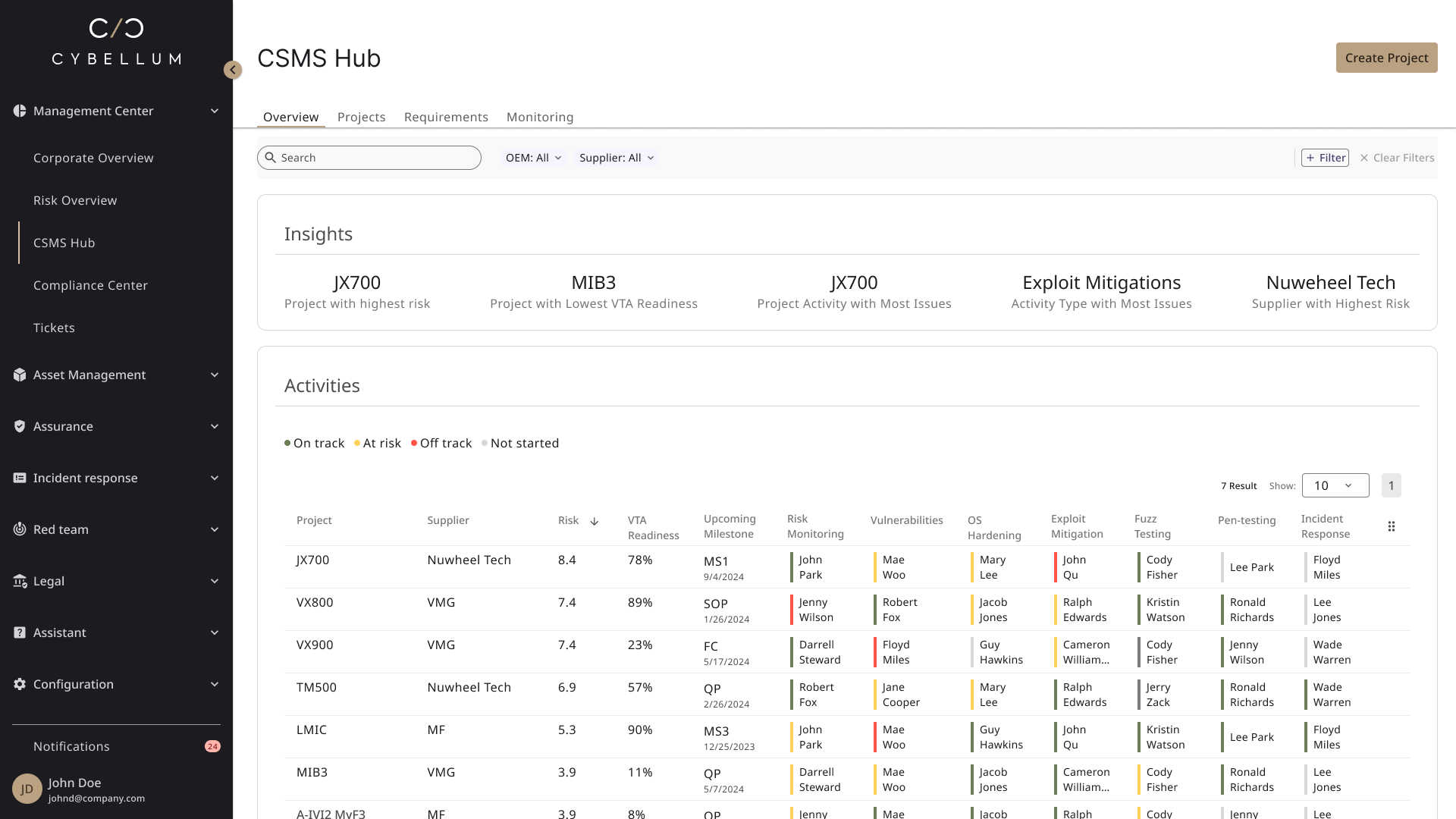
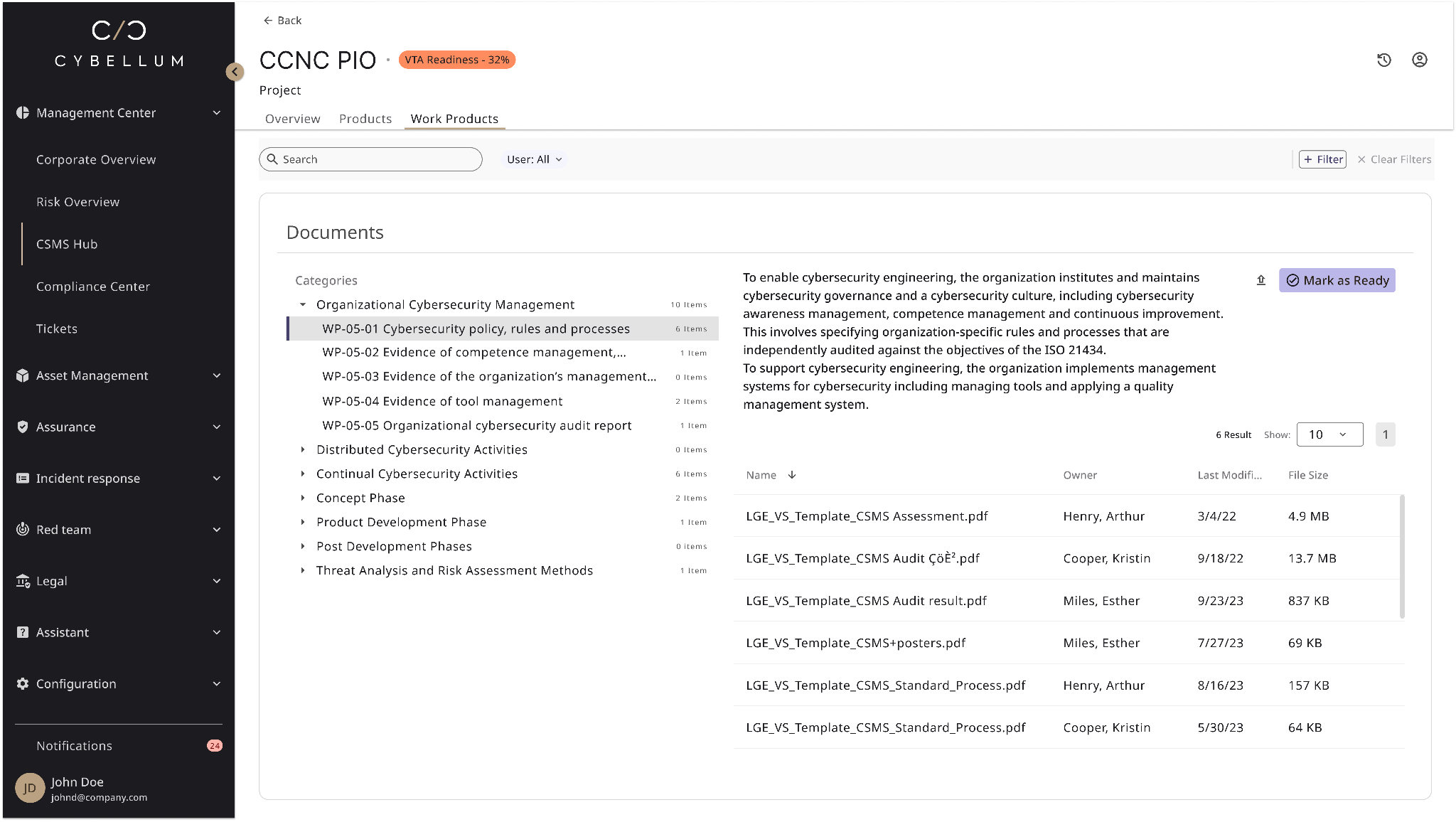
Cybellum plays a pivotal role in aiding organizations to comply with ISO 21434 with a streamlined approach, and a CSMS Cockpit that was developed together with LG Vehicle Component Solutions.
Their solutions offer a streamlined approach to managing and mitigating vehicle cyber risks effectively. Including:
- Visibility and control over all CSMS activities
- An automated & centralized evidence-creation process
- A faster way to make data-driven decisions
- A proven workflow for both automotive OEMs and suppliers
What is TARA (Threat and Risk Assessment)?
TARA stands at the forefront of ISO 21434, providing a structured framework to identify, assess, and prioritize cybersecurity threats and vulnerabilities. This process is not just a one-time assessment but a continuous practice that adapts as new threats emerge and technology evolves. TARA ensures that every potential risk is accounted for and managed appropriately, making it an indispensable tool for automotive cybersecurity.
The implementation of TARA involves various components, including threat intelligence gathering, vulnerability analysis, and risk evaluation. These components work together to create a comprehensive view of the cybersecurity landscape, guiding manufacturers in implementing robust security measures. The accompanying diagram provides a clear visualization of TARA’s integral elements and their interplay within the ISO 21434 framework.
Steps to Implement TARA for ISO 21434 Compliance
Successfully implementing TARA within the ISO 21434 framework involves a series of strategic steps. Initially, it requires an in-depth understanding of the vehicle’s architecture and potential attack surfaces. This is followed by threat modeling and risk analysis, where potential threats are identified, and their impacts are assessed. The process then moves to risk evaluation, where the identified risks are prioritized based on their severity and likelihood of occurrence.
Each step in this process is critical and requires a meticulous approach to ensure no potential risk is overlooked. Cybellum’s case study featuring their partnership with itemis offers a practical example of how TARA can be effectively implemented, showcasing the real-world application of these steps.
Common Challenges in ISO 21434 Risk Modeling
Implementing ISO 21434, specifically the TARA process, is not without its challenges. One of the primary challenges is keeping up with the rapidly evolving landscape of cybersecurity threats. As technology advances, so do the methods employed by cyber attackers, making it crucial for organizations to stay ahead with proactive threat identification and mitigation strategies.
Another significant challenge is the integration of cybersecurity considerations into the existing automotive development lifecycle. This requires not only technical adjustments but also a cultural shift within organizations to prioritize cybersecurity as a key component of automotive safety. Understanding these challenges is essential for any organization aiming to comply with ISO 21434 effectively.
Best Practices for Effective TARA in ISO 21434
Adopting best practices is crucial for the effective implementation of TARA within the ISO 21434 framework. One key practice is the establishment of a cross-functional team that includes cybersecurity experts, engineers, and risk management professionals. This collaborative approach ensures a comprehensive understanding of cybersecurity risks and their potential impact on the entire vehicle ecosystem.
Another best practice is the continuous monitoring and updating of the TARA process. As new threats emerge and technologies evolve, it is vital to revisit and revise the risk assessment and mitigation strategies accordingly. This not only helps in maintaining compliance with ISO 21434 but also ensures that the vehicles remain secure against emerging cyber threats.
Moving forward with Automation
In the intricate dance of automotive cybersecurity, the role of automation cannot be overstated. Automating product security practices is a force multiplier, liberating teams from the time-consuming tasks of manual monitoring and analysis. This liberation is not just about efficiency; it’s about efficacy. With automation, cybersecurity teams can devote their resources and attention to conducting thorough TARA activities, which are pivotal in keeping both people and products safe.
The implementation of TARA within the framework of ISO 21434 is more than a compliance checkbox; it’s a commitment to safety and security in an increasingly connected world. By harnessing the power of automated solutions like those offered by Cybellum, organizations can ensure that their risk assessment is not just comprehensive, but also continually evolving with the landscape of cyber threats. This proactive approach to cybersecurity safeguards not just the vehicles, but also the trust and well-being of consumers.
In essence, the future of automotive cybersecurity hinges on the ability to balance technological advancement with robust security measures. By automating mundane aspects of product security, teams can focus on the nuanced and critical aspects of TARA, ensuring that safety and security are not competing priorities, but harmonious elements in the creation of reliable and resilient automotive products. In this way, the industry can stride forward, confidently navigating the complexities of cybersecurity while keeping the safety of people and products at the forefront.
Learn more about how our automotive-ready Product Security Platform can boost your team, or schedule a demo.