The European Cybersecurity Certification Scheme on Common Criteria (EUCC) represents a pivotal initiative by the European Union to standardize cybersecurity certifications across the continent, ensuring that all ICT products and services meet a unified security benchmark. With the final reworked publication on January 31, 2024, the EUCC aims to enhance product security across Europe’s infrastructure and manufacturing facilities with a transparent and rigorous certification process, mirroring the objectives of the ISO/IEC 15408-1 Common Criteria.
Similar to the FCC’s IoT Security Labeling Program in the US, the EUCC emerges as a strategic response to unify and elevate cybersecurity standards across Europe. By harmonizing certification processes, the EUCC facilitates a coherent security landscape, enabling ICT products to be assessed against a common set of criteria. This initiative not only promotes a high level of security across member states but also aligns with global standards, enhancing interoperability and trust in European ICT products.
Why is the EUCC rolling out?
The European Common Criteria-based Cybersecurity Certification Scheme (EUCC) is part of the greater Cyber Resilience Act, which focuses on securing the collection, storage, and transfer of data.
While in the future this will include cloud computing (EUCS) and 5G mobile networks(EU5G), EUCC is the first of the three to be rolled out, ensuring the security of devices that have a separate security component built into them, such as medical devices.
The development of these schemes is a long process, taking into account consumer needs, legislative goals, and industry capabilities. Involved groups include the European Commission, European Cybersecurity Certificate Group (ECCG), Stakeholder Cybersecurity Certification Group (SCCG), European Agency for Cybersecurity (ENISA), and an Ad-Hoc Working Group.
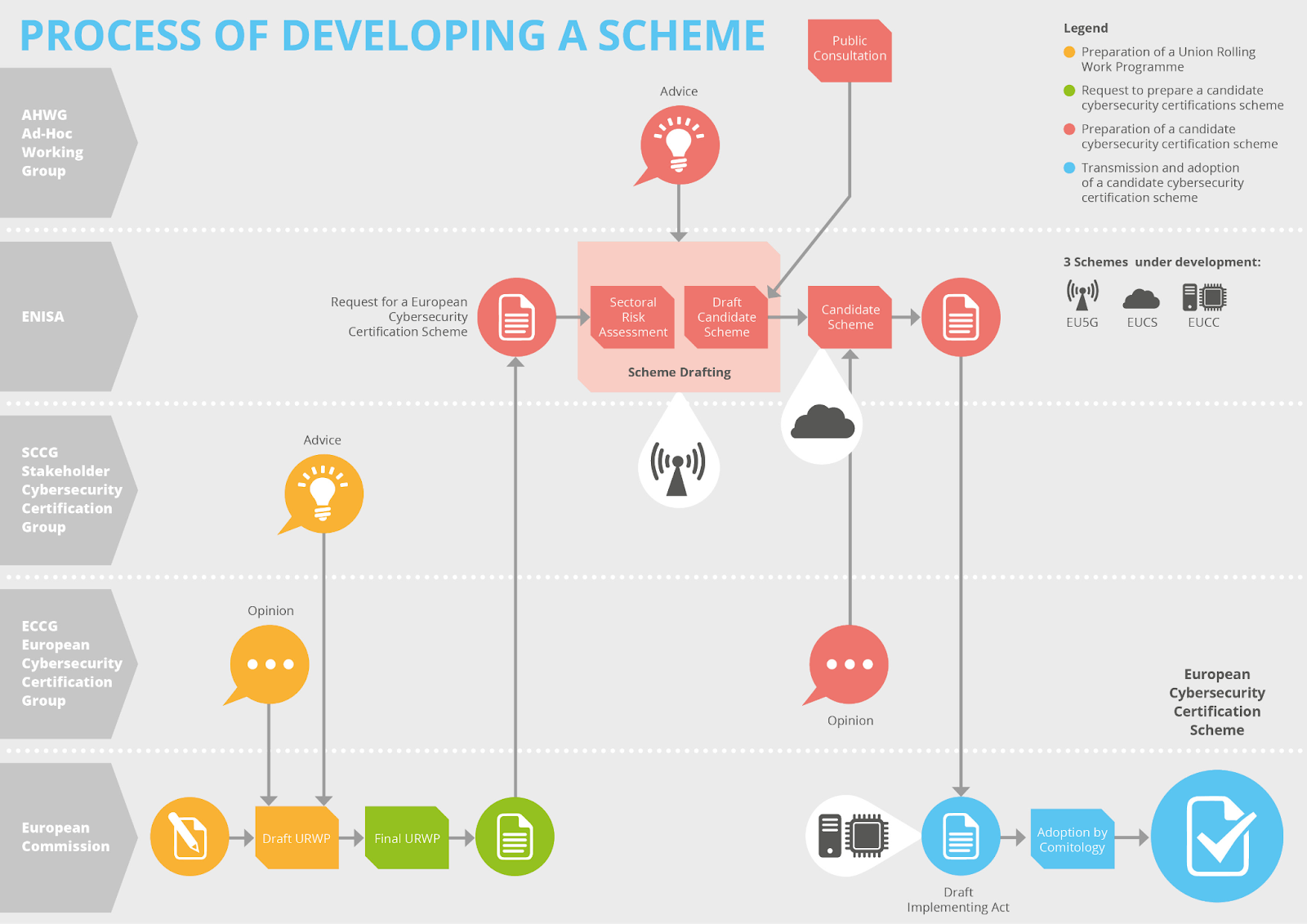
Rooted in the ISO/IEC 15408-1 Common Criteria for Information Technology Security Evaluation, the EUCC serves as a comprehensive framework for the evaluation and certification of ICT products’ security features. It is structured around two fundamental components: Protection Profiles (PPs) and Evaluation Assurance Levels (EALs).
Protection profiles
Protection Profiles outline specific security requirements tailored to different types of ICT products, ensuring that each product category addresses relevant security challenges.
These protection profiles (PPs) act like a standardized set of security goals and hurdles that products need to overcome to be considered secure as a whole- not a plan for individual devices. According to NIST, PPs help standardize the security benchmarks for a product type, facilitating the evaluation process for certifying products that meet those benchmarks. Components of a PP typically include details on security threats, objectives, required security functionalities, and the level of assurance needed to validate those functionalities.
Evaluation Assurance Levels (EALs)
Evaluation Assurance Levels provide a graded scale, from EAL1 to EAL7, indicating the depth and rigor of the evaluation process. This gradation allows vendors and users to understand the extent to which a product has been tested, although it’s important to note that a higher EAL does not necessarily imply a higher level of security, but rather a more thorough examination of the product’s claimed security features.
Unifying cybersecurity requirements across the EU
The EUCC’s adoption is set against the backdrop of a diverse and fragmented cybersecurity landscape in Europe, where different countries have historically adopted varying standards and certification processes.
By introducing a unified certification scheme, the EUCC aims to eliminate these inconsistencies, facilitating a single market for secure ICT products across the EU. This not only simplifies the regulatory environment for manufacturers but also enhances the trust of consumers and businesses in the security of ICT products, thereby fostering a more resilient digital ecosystem.
Critical needs addressed by the EUCC
In today’s digital age, where cyber threats are becoming increasingly sophisticated and pervasive, the relevance of a unified cybersecurity certification scheme like the EUCC cannot be overstated. The scheme addresses several critical needs within the European cybersecurity landscape.
1. Creates a common standard for product security across the EU
By establishing a common standard for cybersecurity certification, the EUCC ensures that all ICT products and services across EU member states meet a consistent level of security. This standardization is crucial for protecting critical infrastructures and sensitive information against evolving cyber threats.
2. Simplifies market access for ICT products
The EUCC facilitates market access for ICT product vendors. With a single certification recognized across the EU, vendors can avoid the time-consuming and costly process of obtaining multiple certifications for different markets. This not only streamlines the path to market for innovative products but also encourages the development and adoption of advanced security technologies.
3. Ensures product security safety for business and consumers
The EUCC enhances consumer and business confidence in ICT products. In an environment where digital threats can undermine trust in technology, a recognized and rigorous certification scheme assures users that certified products have undergone extensive evaluation and are deemed secure for their intended use.
4. Establishes trust that fosters international collaboration
The EUCC aligns with global cybersecurity standards, thereby ensuring that European ICT products remain competitive and trusted on the international stage. This alignment is particularly important in fostering international collaborations and in ensuring that European businesses can operate effectively in a global marketplace.
EUCC certification process and relevancy
The certification process under the EUCC begins with vendors completing a Security Target (ST) description for their product. This document outlines the product’s security features, evaluates potential security threats, and details how the product conforms to the relevant Protection Profile and Evaluation Assurance Level.
This initial step is crucial, particularly for products that incorporate specific security functionalities, such as smart cards and hardware devices with security boxes. These products often rely on specialized hardware elements or physical security measures to protect against direct attacks. The ST allows vendors to clearly articulate how their products address these security requirements and how they plan to mitigate identified risks.
Once the ST is submitted, the product undergoes a thorough evaluation by an accredited laboratory. This evaluation is not merely a verification of the product’s security features but also includes a comprehensive assessment of how well the product meets the specifications defined in the Protection Profile. The evaluation process is meticulous, ensuring that all aspects of the product’s security are scrutinized and that any claims made by the vendor are independently verified.
The relevance of this certification process lies in its ability to provide a clear and reliable indicator of a product’s security. For government agencies, businesses, and consumers, the EUCC certification serves as a seal of approval, indicating that a product has been rigorously tested and meets the stringent security standards set forth by the EU. This, in turn, facilitates informed decision-making and contributes to the overall security and resilience of Europe’s digital infrastructure.

Scoring methodology
The scoring methodology under the EUCC is derived from the Common Criteria’s vulnerability assessment components, specifically the AVA_VAN family, which ranges from AVA_VAN.1 to AVA_VAN.5. These components provide a structured approach to evaluating the vulnerabilities of ICT products, taking into account various factors that could influence the product’s security.
The components are designed to correspond to different levels of assurance, allowing for a nuanced assessment of a product’s vulnerability to potential threats. This correspondence ensures that the level of scrutiny applied during the evaluation is proportionate to the risks associated with the product’s intended use.
The scoring methodology considers several critical factors, including:
- Elapsed Time: The time required to identify and exploit a vulnerability, which can significantly impact the feasibility of an attack.
- Specialist Expertise: The level of technical skill needed to exploit a vulnerability, with higher requirements potentially limiting the number of capable attackers.
- Knowledge of the TOE: Familiarity with the Target of Evaluation’s design and operation, which can facilitate or hinder an attack.
- Window of Opportunity: The timeframe during which an attack is feasible, influenced by factors such as the availability of the product and the presence of mitigating controls.
- Required Equipment: The necessity for specific hardware or software to exploit a vulnerability, which can act as a barrier to potential attackers.
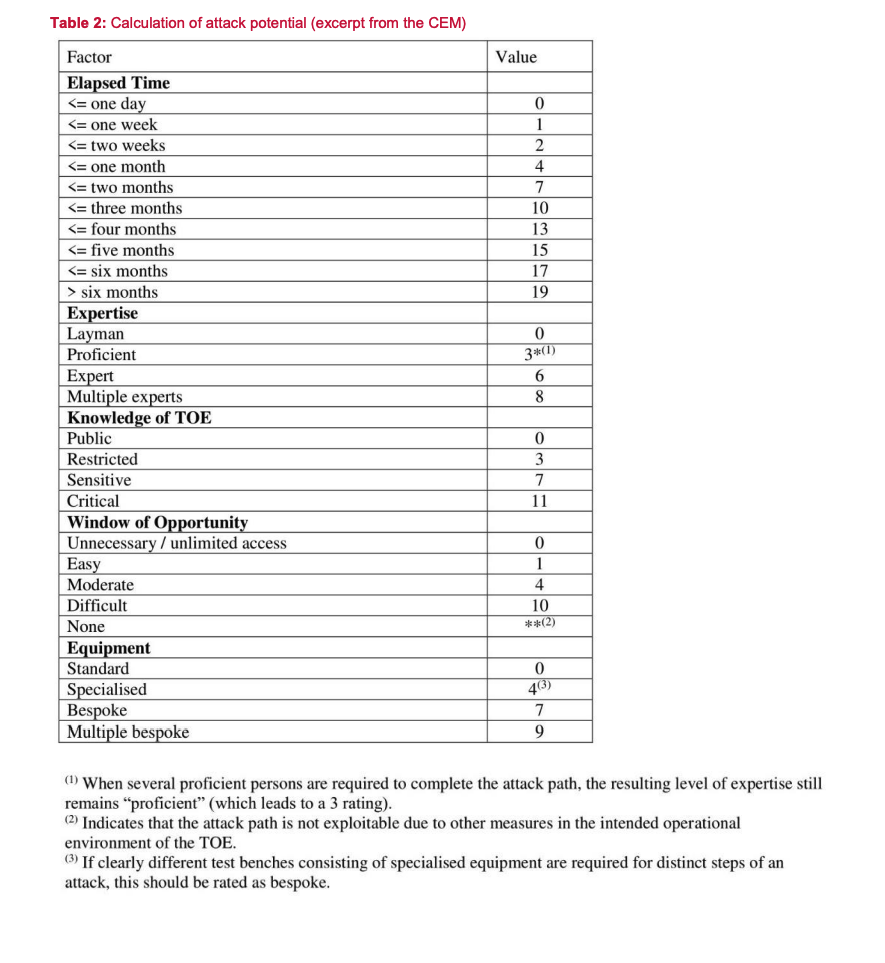
By considering these factors, the scoring methodology provides a comprehensive and nuanced view of a product’s security posture. This approach ensures that the certification process not only assesses the presence of security features but also evaluates their effectiveness in the context of real-world threats.
EUCC Reporting Requirements
The EUCC sets forth stringent reporting requirements for certificate holders, emphasizing the importance of transparency and accountability in managing cybersecurity risks. Certificate holders are required to produce a vulnerability impact analysis report whenever an analysis indicates that a vulnerability could affect the conformity of the ICT product with its certification.
This report must assess several key elements, including:
- The impact of the vulnerability on the certified ICT product.
- The potential risks associated with the vulnerability and consider factors such as the likelihood of exploitation and the severity of potential impacts.
- The feasibility of remedying the vulnerability, including an evaluation of possible mitigation strategies or corrective actions.
These reporting requirements are consistent with broader regulatory frameworks, such as the EU Cybersecurity Act (CRA) mentioned above and the Directive on Security of Network and Information Systems (NIS2). By aligning with these frameworks, the EUCC ensures a coordinated and effective response to vulnerabilities, enhancing the overall security of certified ICT products.
In addition to vulnerability reporting, the EUCC emphasizes the importance of remediation. Certificate holders are obligated to propose appropriate remedial actions to the certification body, which then reviews the certificate in light of the proposed remedies. This process ensures that vulnerabilities are not only identified and reported but also actively addressed, maintaining the integrity and security of certified products.
Moreover, the inclusion of patch management in the certification process acknowledges the dynamic nature of cybersecurity threats. By allowing for the certification of patch mechanisms, the EUCC recognizes that security is an ongoing process and that certified products must be able to adapt to emerging threats while maintaining their certified security posture.
Bolstering product security
Focusing specifically on product security, manufacturers who wish to operate or conduct business within the European Union will have to mature the way they collect and process data information to ensure a continuous level of elevated cybersecurity. This, in turn, enhances the resilience of Europe’s digital infrastructure, fosters consumer and business confidence in ICT products, and supports the development of a competitive and secure digital market in Europe.
As the implementation date approaches, the importance of the EUCC in shaping a secure and cohesive digital landscape in Europe becomes increasingly clear, underscoring the need for continued commitment and collaboration among all stakeholders in the cybersecurity ecosystem.